Join Membership
Join Membership
We Are Now Open On Saturdays
50% off all dental treatments and 25% all medical services amazing value for only £20 a month
Bacterial infections arise when harmful bacteria enter the body and begin to multiply, causing illness. Antibiotics can be used to treat bacterial infections, as opposed to viral infections, which are caused by viruses.
These infections can impact different areas of the body and vary in severity from mild to serious. Because of this, our Clinic is committed to providing diagnosis and treatment to help prevent further complications.

Bacterial infections are categorized into:
Signs of infection can differ based on the type of infection. The common ones include:
Certain bacterial infections, like chlamydia and non-gonococcal urethritis (NGU), may not show any symptoms. In addition, some infections present different symptoms in both men and women.
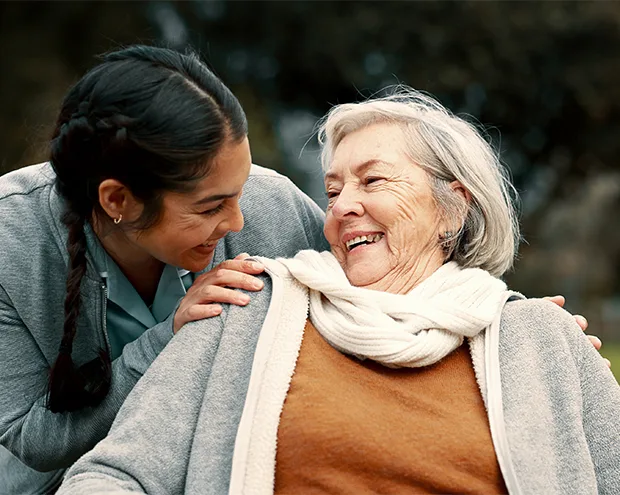
We’re here to help - get in touch or book your appointment today.
To lower your risk of bacterial infections, maintain proper hygiene by frequently washing your hands and handling food safely. Also, staying updated on vaccinations is crucial because some bacterial infections are preventable through immunization.
To lower your risk of exposure, stay away from close contact with those who exhibit signs of infections.
Inadequate handwashing can allow bacteria to enter the body.
Some bacteria such as those causing gonorrhea or chlamydia can be transmitted through sexual contact.
Scrapes, cuts, or other skin injuries can become infected when bacteria enter through these breaks.
Eating or drinking anything contaminated with harmful bacteria may cause gastrointestinal infections.
Environments with high crowd density or poor sanitation can heighten the risk of bacterial infections.
Direct skin-to-skin contact, or respiratory droplets from an infected individual are the most likely ways for bacteria to spread.
The following medical conditions can raise the risk of infections:
When antibiotics are used excessively or inappropriately, resistant bacteria can develop; making infections more difficult to cure.
Conditions including diabetes, HIV/AIDS, and cancer therapies can impair immunity, leaving the body more vulnerable to bacterial infections.
Long-term illnesses such as cystic fibrosis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) can make people more vulnerable to bacterial infections, especially in the lungs.
Identifying the cause of your bacterial infection-related symptoms is essential for effective treatment and relief. Book an appointment with one of our doctors to determine the best course of action.